JSON框架之FastJson的用法和实例
1.1.FastJson的介绍:
JSON协议使用方便,越来越流行,JSON的处理器有很多,这里我介绍一下FastJson,FastJson是阿里的开源框架,被不少企业使用,是一个极其优秀的Json框架,Github地址: FastJson
1.2.FastJson的特点:
1.FastJson数度快,无论序列化和反序列化,都是当之无愧的fast
2.功能强大(支持普通JDK类包括任意Java Bean Class、Collection、Map、Date或enum)
3.零依赖(没有依赖其它任何类库)
1.3.FastJson的简单说明:
FastJson对于json格式字符串的解析主要用到了下面三个类:
1.JSON:fastJson的解析器,用于JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间的转换
2.JSONObject:fastJson提供的json对象
3.JSONArray:fastJson提供json数组对象
还在迷茫和彷徨吗,快上车,老司机带你飞!
2.FastJson的用法
首先定义三个json格式的字符串
//json字符串-简单对象型
private static final String JSON_OBJ_STR = "{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12}";
//json字符串-数组类型
private static final String JSON_ARRAY_STR = "[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]";
//复杂格式json字符串
private static final String COMPLEX_JSON_STR = "{\"teacherName\":\"crystall\",\"teacherAge\":27,\"course\":{\"courseName\":\"english\",\"code\":1270},\"students\":[{\"studentName\":\"lily\",\"studentAge\":12},{\"studentName\":\"lucy\",\"studentAge\":15}]}";fastJson对于json格式字符串的解析主要用到了一下三个类:
JSON:fastJson的解析器,用于JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间的转换。
JSONObject:fastJson提供的json对象。
JSONArray:fastJson提供json数组对象。
我们可以把JSONObject当成一个Map<String,Object>来看,只是JSONObject提供了更为丰富便捷的方法,方便我们对于对象属性的操作。我们看一下源码。

同样我们可以把JSONArray当做一个List<Object>,可以把JSONArray看成JSONObject对象的一个集合。
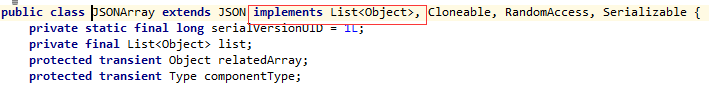
此外,由于JSONObject和JSONArray继承了JSON,所以说也可以直接使用两者对JSON格式字符串与JSON对象及javaBean之间做转换,不过为了避免混淆我们还是使用JSON。
2.1.JSON格式字符串与JSON对象之间的转换
2.1.1.json字符串-简单对象型与JSONObject之间的转换
/**
* json字符串-简单对象型到JSONObject的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONStrToJSONObject() {
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR);
System.out.println("studentName: " + jsonObject.getString("studentName") + ":" + " studentAge: "
+ jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge"));
}/**
* JSONObject到json字符串-简单对象型的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONObjectToJSONStr() { //已知JSONObject,目标要转换为json字符串
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); // 第一种方式
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(jsonObject); // 第二种方式
//String jsonString = jsonObject.toJSONString();
System.out.println(jsonString);
}2.1.2.json字符串(数组类型)与JSONArray之间的转换
/**
* json字符串-数组类型到JSONArray的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONStrToJSONArray() {
JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR); //遍历方式1
int size = jsonArray.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
System.out.println("studentName: " + jsonObject.getString("studentName") + ":" + " studentAge: "
+ jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge"));
} //遍历方式2
for (Object obj : jsonArray) {
JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) obj;
System.out.println("studentName: " + jsonObject.getString("studentName") + ":" + " studentAge: "
+ jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge"));
}
}/**
* JSONArray到json字符串-数组类型的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONArrayToJSONStr() { //已知JSONArray,目标要转换为json字符串
JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR); //第一种方式
String jsonString = JSONArray.toJSONString(jsonArray); // 第二种方式
//String jsonString = jsonArray.toJSONString(jsonArray);
System.out.println(jsonString);
}2.1.3.复杂json格式字符串与JSONObject之间的转换
/**
* 复杂json格式字符串到JSONObject的转换
*/@Testpublic void testComplexJSONStrToJSONObject() {
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR);
String teacherName = jsonObject.getString("teacherName");
Integer teacherAge = jsonObject.getInteger("teacherAge");
System.out.println("teacherName: " + teacherName + " teacherAge: " + teacherAge);
JSONObject jsonObjectcourse = jsonObject.getJSONObject("course"); //获取JSONObject中的数据
String courseName = jsonObjectcourse.getString("courseName");
Integer code = jsonObjectcourse.getInteger("code");
System.out.println("courseName: " + courseName + " code: " + code);
JSONArray jsonArraystudents = jsonObject.getJSONArray("students"); //遍历JSONArray
for (Object object : jsonArraystudents) {
JSONObject jsonObjectone = (JSONObject) object;
String studentName = jsonObjectone.getString("studentName");
Integer studentAge = jsonObjectone.getInteger("studentAge");
System.out.println("studentName: " + studentName + " studentAge: " + studentAge);
}
}/**
* 复杂JSONObject到json格式字符串的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONObjectToComplexJSONStr() { //复杂JSONObject,目标要转换为json字符串
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR); //第一种方式
//String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(jsonObject);
//第二种方式
String jsonString = jsonObject.toJSONString();
System.out.println(jsonString);
}2.2.JSON格式字符串与javaBean之间的转换
2.2.1.json字符串-简单对象型与javaBean之间的转换
/**
* json字符串-简单对象到JavaBean之间的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONStrToJavaBeanObj() { //第一种方式
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR);
String studentName = jsonObject.getString("studentName");
Integer studentAge = jsonObject.getInteger("studentAge"); //Student student = new Student(studentName, studentAge);
//第二种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类
//Student student = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, new TypeReference<Student>() {});
//第三种方式,使用Gson的思想
Student student = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR, Student.class);
System.out.println(student);
}/**
* JavaBean到json字符串-简单对象的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJavaBeanObjToJSONStr() {
Student student = new Student("lily", 12);
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(student);
System.out.println(jsonString);
}2.2.2.json字符串-数组类型与javaBean之间的转换
/**
* json字符串-数组类型到JavaBean_List的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONStrToJavaBeanList() { //第一种方式
JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR); //遍历JSONArray
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student student = null; for (Object object : jsonArray) {
JSONObject jsonObjectone = (JSONObject) object;
String studentName = jsonObjectone.getString("studentName");
Integer studentAge = jsonObjectone.getInteger("studentAge");
student = new Student(studentName,studentAge);
students.add(student);
}
System.out.println("students: " + students); //第二种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类
List<Student> studentList = JSONArray.parseObject(JSON_ARRAY_STR, new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {});
System.out.println("studentList: " + studentList); //第三种方式,使用Gson的思想
List<Student> studentList1 = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR, Student.class);
System.out.println("studentList1: " + studentList1);
}/**
* JavaBean_List到json字符串-数组类型的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJavaBeanListToJSONStr() {
Student student = new Student("lily", 12);
Student studenttwo = new Student("lucy", 15);
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
students.add(student);
students.add(studenttwo);
String jsonString = JSONArray.toJSONString(students);
System.out.println(jsonString);
}2.2.3.复杂json格式字符串与与javaBean之间的转换
/**
* 复杂json格式字符串到JavaBean_obj的转换
*/@Testpublic void testComplexJSONStrToJavaBean(){ //第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类
Teacher teacher = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});
System.out.println(teacher); //第二种方式,使用Gson思想
Teacher teacher1 = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, Teacher.class);
System.out.println(teacher1);
}/**
* 复杂JavaBean_obj到json格式字符串的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJavaBeanToComplexJSONStr(){ //已知复杂JavaBean_obj
Teacher teacher = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR, new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(teacher);
System.out.println(jsonString);
}2.3.javaBean与json对象间的之间的转换
2.3.1.简单javaBean与json对象之间的转换
/**
* 简单JavaBean_obj到json对象的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJavaBeanToJSONObject(){ //已知简单JavaBean_obj
Student student = new Student("lily", 12); //方式一
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(student);
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
System.out.println(jsonObject); //方式二
JSONObject jsonObject1 = (JSONObject) JSONObject.toJSON(student);
System.out.println(jsonObject1);
}/**
* 简单json对象到JavaBean_obj的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJSONObjectToJavaBean(){ //已知简单json对象
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(JSON_OBJ_STR); //第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类
Student student = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), new TypeReference<Student>() {});
System.out.println(student); //第二种方式,使用Gson的思想
Student student1 = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), Student.class);
System.out.println(student1);
}2.3.2.JavaList与JsonArray之间的转换
/**
* JavaList到JsonArray的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJavaListToJsonArray() { //已知JavaList
Student student = new Student("lily", 12);
Student studenttwo = new Student("lucy", 15);
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
students.add(student);
students.add(studenttwo); //方式一
String jsonString = JSONArray.toJSONString(students);
JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(jsonString);
System.out.println(jsonArray); //方式二
JSONArray jsonArray1 = (JSONArray) JSONArray.toJSON(students);
System.out.println(jsonArray1);
}/**
* JsonArray到JavaList的转换
*/@Testpublic void testJsonArrayToJavaList() { //已知JsonArray
JSONArray jsonArray = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON_ARRAY_STR); //第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类
ArrayList<Student> students = JSONArray.parseObject(jsonArray.toJSONString(), new TypeReference<ArrayList<Student>>() {});
System.out.println(students); //第二种方式,使用Gson的思想
List<Student> students1 = JSONArray.parseArray(jsonArray.toJSONString(), Student.class);
System.out.println(students1);
}2.3.3.复杂JavaBean_obj与json对象之间的转换
/**
* 复杂JavaBean_obj到json对象的转换
*/@Testpublic void testComplexJavaBeanToJSONObject() { //已知复杂JavaBean_obj
Student student = new Student("lily", 12);
Student studenttwo = new Student("lucy", 15);
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
students.add(student);
students.add(studenttwo);
Course course = new Course("english", 1270);
Teacher teacher = new Teacher("crystall", 27, course, students); //方式一
String jsonString = JSONObject.toJSONString(teacher);
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonString);
System.out.println(jsonObject); //方式二
JSONObject jsonObject1 = (JSONObject) JSONObject.toJSON(teacher);
System.out.println(jsonObject1);
}/**
* 复杂json对象到JavaBean_obj的转换
*/@Testpublic void testComplexJSONObjectToJavaBean() { //已知复杂json对象
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONObject.parseObject(COMPLEX_JSON_STR); //第一种方式,使用TypeReference<T>类,由于其构造方法使用protected进行修饰,故创建其子类
Teacher teacher = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), new TypeReference<Teacher>() {});
System.out.println(teacher); //第二种方式,使用Gson的思想
Teacher teacher1 = JSONObject.parseObject(jsonObject.toJSONString(), Teacher.class);
System.out.println(teacher1);
}此外的:
1,对于JSON对象与JSON格式字符串的转换可以直接用 toJSONString()这个方法。
2,javaBean与JSON格式字符串之间的转换要用到:JSON.toJSONString(obj);
3,javaBean与json对象间的转换使用:JSON.toJSON(obj),然后使用强制类型转换,JSONObject或者JSONArray。
另一实例:
package junit.test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
/*
* 这里将json的转化和解析都放在一起了,大家可以根据实际需要来转化json字符串和解析json字符串
*/
public class TestFastJson {
static class Person{
private String id ;
private String name;
private int age ;
public Person(){
}
public Person(String id,String name,int age){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [age=" + age + ", id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
method2();
method3();
method4();
}
static void method1(){
System.out.println("javabean转化示例开始----------");
Person person = new Person("1","fastjson",1);
//这里将javabean转化成json字符串
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(person);
System.out.println(jsonString);
//这里将json字符串转化成javabean对象,
person =JSON.parseObject(jsonString,Person.class);
System.out.println(person.toString());
System.out.println("javabean转化示例结束----------");
}
static void method2(){
System.out.println("List<javabean>转化示例开始----------");
Person person1 = new Person("1","fastjson1",1);
Person person2 = new Person("2","fastjson2",2);
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<Person>();
persons.add(person1);
persons.add(person2);
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(persons);
System.out.println("json字符串:"+jsonString);
//解析json字符串
List<Person> persons2 = JSON.parseArray(jsonString,Person.class);
//输出解析后的person对象,也可以通过调试模式查看persons2的结构
System.out.println("person1对象:"+persons2.get(0).toString());
System.out.println("person2对象:"+persons2.get(1).toString());
System.out.println("List<javabean>转化示例结束----------");
}
static void method3(){
System.out.println("List<String>转化示例开始----------");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("fastjson1");
list.add("fastjson2");
list.add("fastjson3");
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(list);
System.out.println("json字符串:"+jsonString);
//解析json字符串
List<String> list2 = JSON.parseObject(jsonString,new TypeReference<List<String>>(){});
System.out.println(list2.get(0)+"::"+list2.get(1)+"::"+list2.get(2));
System.out.println("List<String>转化示例结束----------");
}
static void method4(){
System.out.println(" List<Map<String,Object>>转化示例开始 ----------");
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("key1", "value1");
map.put("key2", "value2");
Map<String,Object> map2 = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map2.put("key1", 1);
map2.put("key2", 2);
List<Map<String,Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String,Object>>();
list.add(map);
list.add(map2);
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(list);
System.out.println("json字符串:"+jsonString);
//解析json字符串
List<Map<String,Object>> list2 = JSON.parseObject(jsonString,new TypeReference<List<Map<String,Object>>>(){});
System.out.println("map的key1值"+list2.get(0).get("key1"));
System.out.println("map的key2值"+list2.get(0).get("key2"));
System.out.println("ma2p的key1值"+list2.get(1).get("key1"));
System.out.println("map2的key2值"+list2.get(1).get("key2"));
}
}如对本文有疑问,请提交到交流论坛,广大热心网友会为你解答!! 点击进入论坛

